Science Friday

Covering the outer reaches of space to the tiniest microbes in our bodies, Science Friday is the source for entertaining and educational stories about science, technology, and other cool stuff.
Website : https://www.wnycstudios.org/podcasts/science-friday
RSS Feed : https://feeds.feedburner.com/science-friday/
Last Episode : September 17, 2025 10:00am
Last Scanned : 5.3 hours ago

Episodes
Episodes currently hosted on IPFS.
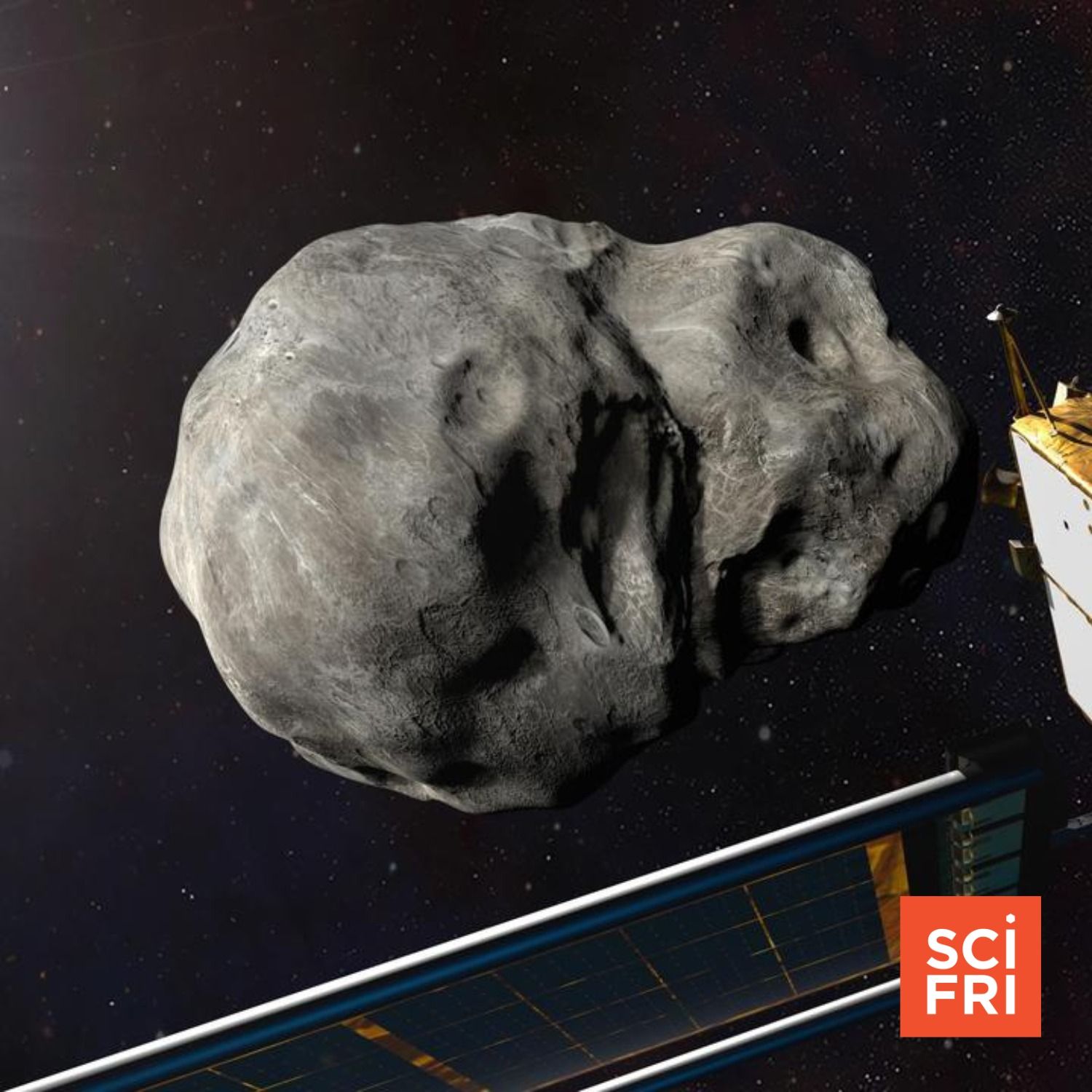 If An Asteroid Were Headed For Earth, Would We Be Ready?
If An Asteroid Were Headed For Earth, Would We Be Ready?Confirmed 4
You might remember news reporting from earlier this year that a 180-foot asteroid had about a 3% chance of hitting Earth in 2032. And if it did, it would unleash energy equivalent to hundreds of nuclear bombs. After further observations, astronomers revised that probability way down, to close to zero. So what is our current capability to spot Earthbound asteroids? And how are governments preparing to communicate and respond to a potential impact on a populated area?Joining Host Ira Flatow with some of the answers are Kelly Fast, from NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office, and Leviticus “L.A.” Lewis, former FEMA liaison for that office.Guests: Dr. Kelly Fast is the acting planetary defense officer in NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office, based in Laurel, Maryland.Leviticus “L.A.” Lewis is a former FEMA liaison to the NASA Planetary Defense Coordination Office.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Expires in 37 hours
Published Wednesday
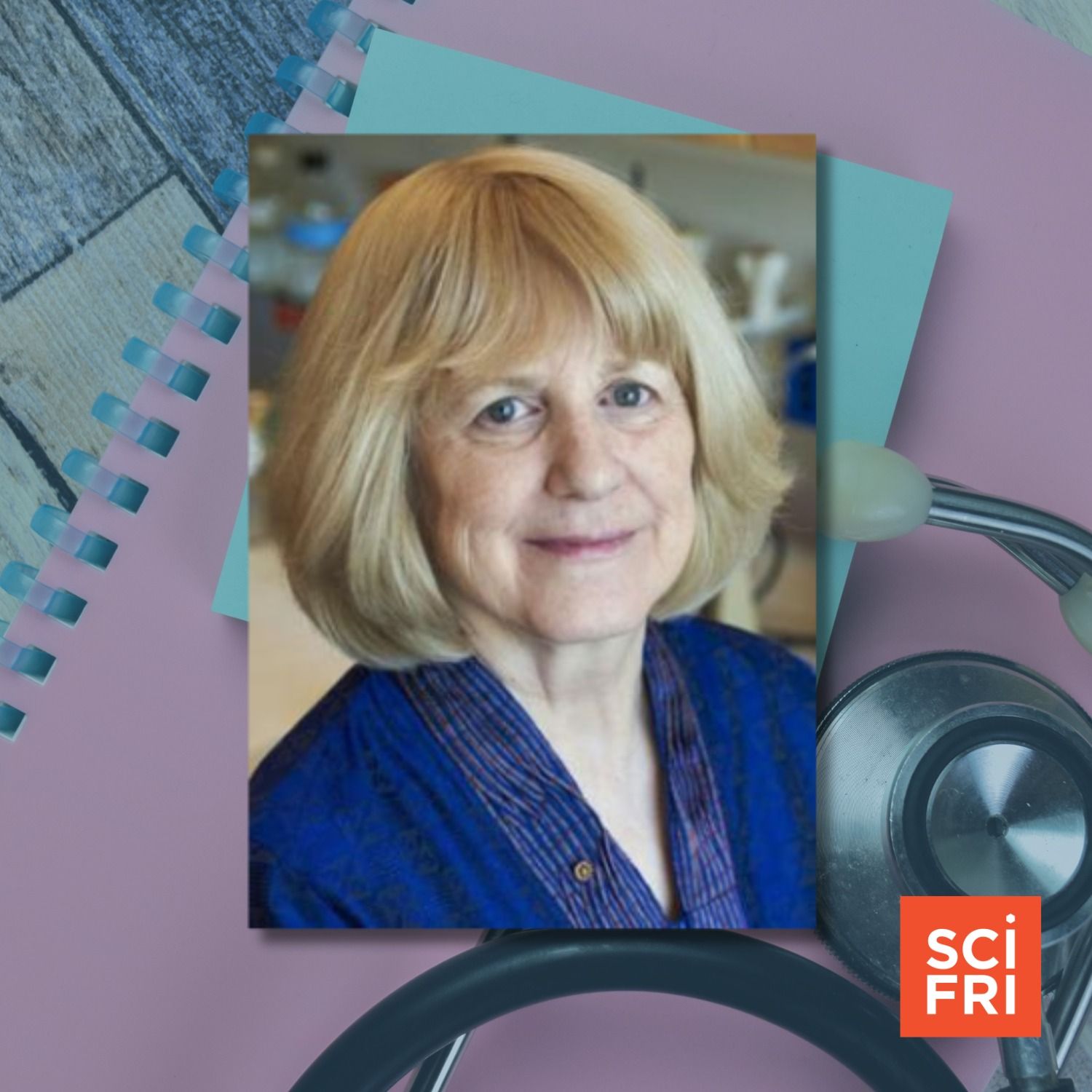 A Trailblazing Geneticist Reflects On Her Life And Work
A Trailblazing Geneticist Reflects On Her Life And WorkProcessing 1
It’s common knowledge that many diseases and conditions have some kind of genetic link. But that wasn't always the case. In 1990, long before the Human Genome Project tied so many health issues to differences in genetics, researchers identified a gene called BRCA1. It was the first gene linked to a hereditary form of any common cancer. People with certain variants of BRCA1 stood a higher risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer than those without those mutations. Geneticist Mary-Claire King and her lab were the first to identify that gene. She joins Host Flora Lichtman to talk about her background, her research, and her approach to science.Guest: Dr. Mary-Claire King is an American Cancer Society Professor in the departments of Genome Sciences and Medicine at the University of Washington in Seattle.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Expires in 16 hours
Published Tuesday
 What The Label Of ‘Genius’ Tells Us About Our Society
What The Label Of ‘Genius’ Tells Us About Our SocietyWhat makes someone a genius? Are they the smartest, most creative, most innovative people? Those with the highest IQ? Who we consider a genius may actually tell us much more about what we value as a society than any objective measure of brilliance. A compelling or quirky life story often shapes who is elevated to genius status.Host Ira Flatow unpacks the complicated and coveted title of genius with Helen Lewis, author of The Genius Myth: A Curious History of A Dangerous Idea.Read an excerpt of The Genius Myth: A Curious History of A Dangerous Idea. Guest: Helen Lewis is a staff writer at The Atlantic, based in London, who writes about politics and culture.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Expires in 16 hours
Published Monday
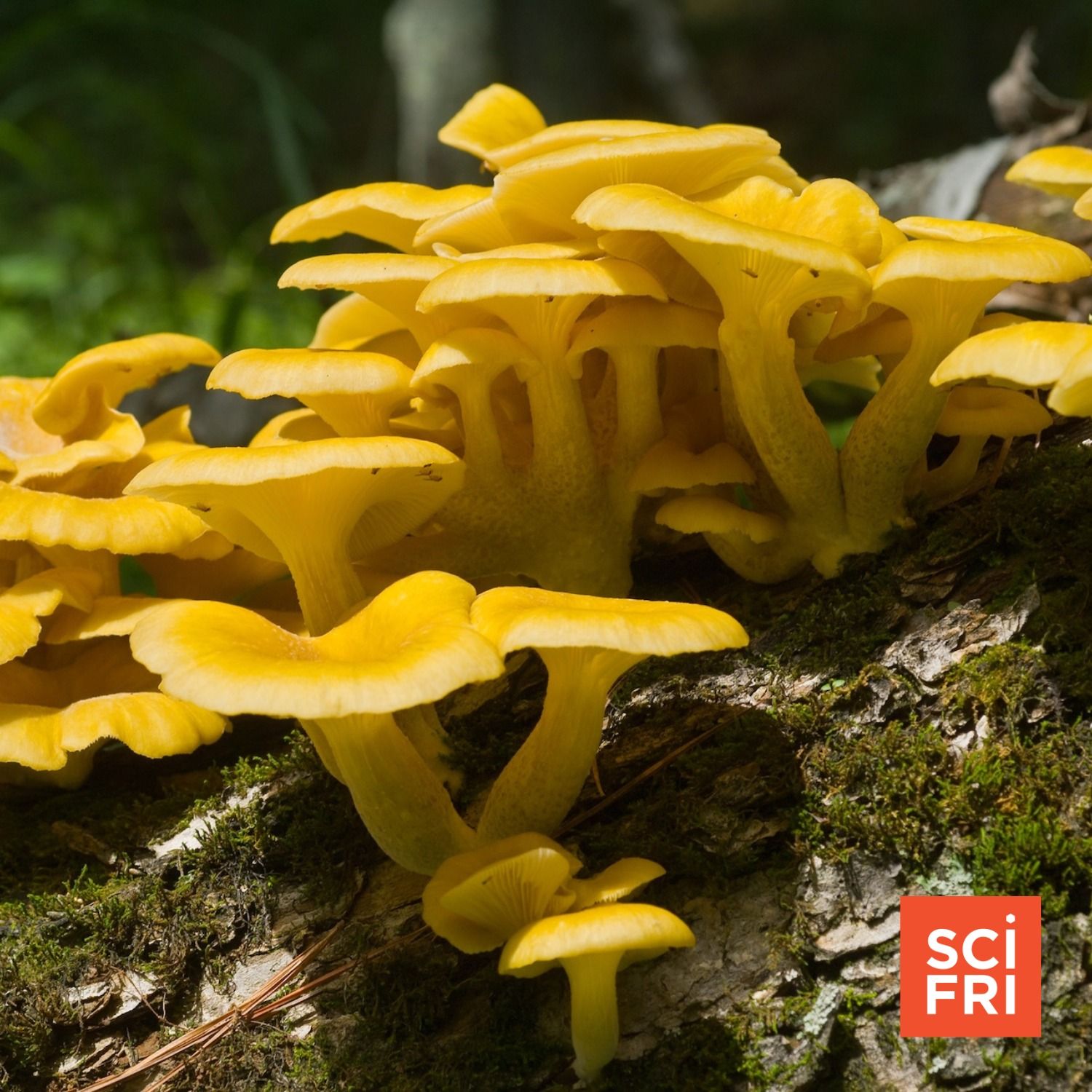 A Delicious But Invasive Mushroom Could Affect Fungal Diversity
A Delicious But Invasive Mushroom Could Affect Fungal DiversityIt all started harmlessly enough: People bought kits to grow mushrooms at home. But then, scientists in the upper Midwest noticed something strange. The golden oyster mushroom, which is not native to the United States, was thriving in local forests. Those homegrown mushrooms escaped our basements into the wild. Fungal ecologist Aishwarya Veerabahu joins Host Ira Flatow to discuss what impact these invasive mushrooms might have on the ecosystem.Plus, nightshade expert Sandra Knapp describes the evolution of the potato plant, and how a lucky crossbreeding millions of years ago may have given rise to the starchy tubers we eat today.Guests:Aishwarya Veerabahu is a fungal ecologist and PhD candidate at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.Dr. Sandra Knapp is a Merit Researcher at the Natural History Museum in London.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published Thursday
 A Photographer Captures Nature In Mind-Boggling Detail
A Photographer Captures Nature In Mind-Boggling DetailIf you’ve flipped through an issue of National Geographic or scrolled through their social media, and caught a stunningly detailed photo of a tiny creature—like one where you can make out the hairs on a honeybee’s eyeballs, or the exact contours of a hummingbird’s forked tongue—you have probably seen the work of Anand Varma. He’s an award-winning science photographer, a National Geographic Explorer, and the founder of WonderLab, a storytelling studio in Berkeley, California.Varma speaks with Host Flora Lichtman and takes us behind the lens to show what it takes to capture iconic images of creatures that are so often overlooked.Guest: Anand Varma is a science photographer, a National Geographic Explorer, and the founder of WonderLab. He’s based in Berkeley, California.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 09/10
 How Shoddy Science Is Driving A Supplement Boom
How Shoddy Science Is Driving A Supplement BoomDietary supplements are big business, with one recent estimate showing the industry is worth almost $64 billion in the United States alone. Take a casual scroll through your social media and you’ll find influencers hawking all kinds of supplements. But how effective are they? How are they regulated? And why are these “natural” remedies so appealing to millions of Americans? To size up the science and culture of supplements, Host Flora Lichtman talks with supplement researcher Pieter Cohen, and Colleen Derkatch, author of Why Wellness Sells: Natural Health in a Pharmaceutical Culture. Guests: Dr. Pieter Cohen is an Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and an internist at the Cambridge Health Alliance where he leads the Supplement Research Program. Dr. Colleen Derkatch is the author of Why Wellness Sells: Natural Health in a Pharmaceutical Culture and professor of rhetoric at Toronto Metropolitan University.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 09/09
 After CDC Director Is Ousted, More Senior Officials Resign
After CDC Director Is Ousted, More Senior Officials ResignOn August 27, Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. and the White House fired CDC director Susan Monarez after only a month on the job. Right after she was ousted, other senior leaders resigned from the agency, including Demetre Daskalakis, an infectious disease physician and former director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the CDC.Dr. Daskalakis speaks with Host Flora Lichtman about the state of the agency and what these developments mean for public health.Guest: Dr. Demetre Daskalakis is the former director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the CDC.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 09/05
 How Common Household Products Pollute Our Indoor Air
How Common Household Products Pollute Our Indoor AirYou have probably given some thought to outdoor air pollution, whether it’s wildfire smoke or smog from traffic. You may even check AQI measurements on your phone. But what about the air inside your home? Host Flora Lichtman talks to civil and environmental engineer Nusrat Jung, who studies indoor air pollution, about how we create toxic air without even knowing it, and what we can do to avoid it. Guest: Dr. Nusrat Jung is a civil and environmental engineer at Purdue University.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 09/03
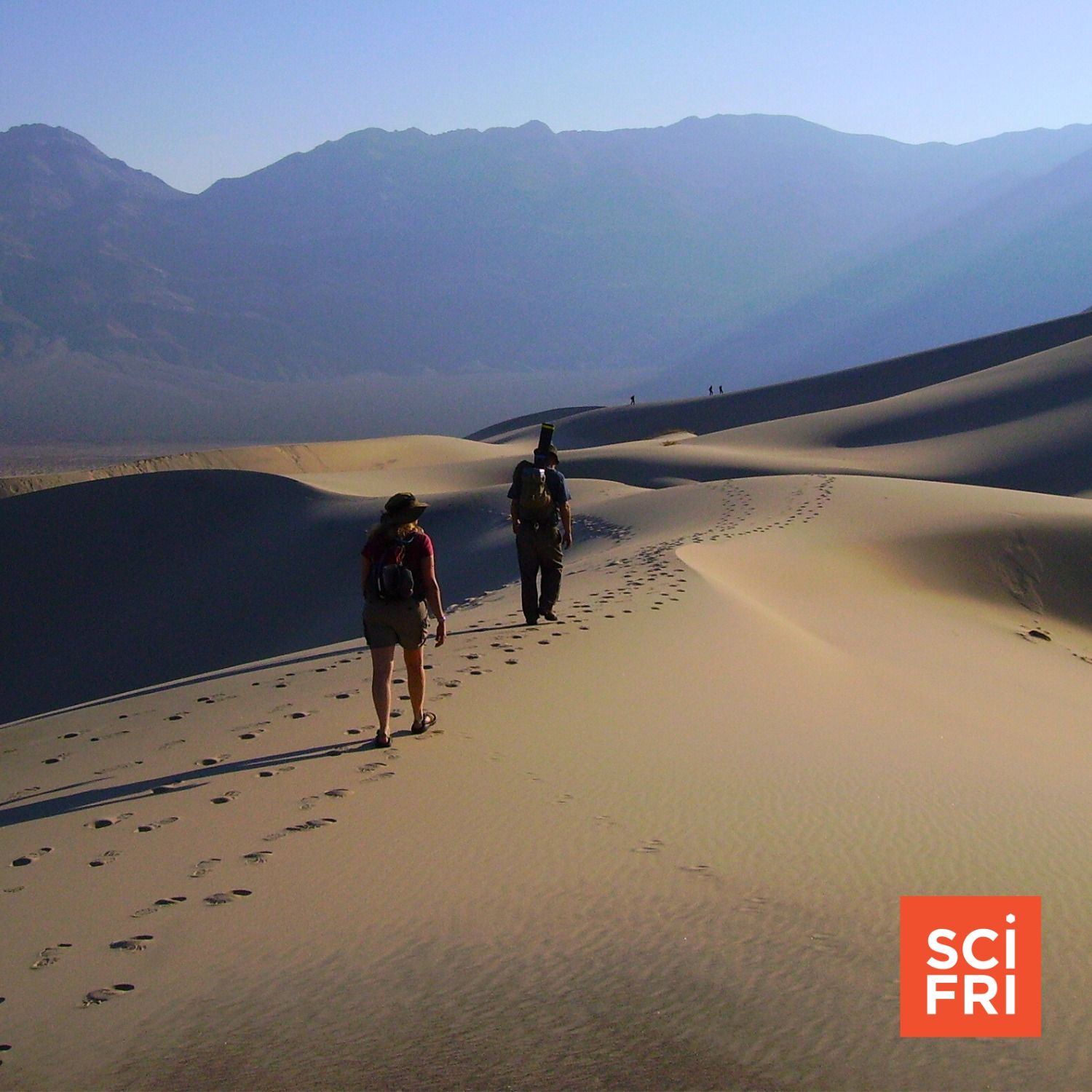 The Shape-Shifting Science Of Sand Dunes
The Shape-Shifting Science Of Sand DunesIn some places, sand dunes protect shorelines from the onslaught of ocean waves. In other places, the dunes themselves are on the move, and threaten human structures.Host Flora Lichtman talks with mechanical engineer Nathalie Vriend, who studies the structure of sand dunes, about what makes a heap of sand a dune, and what scientists still hope to learn about sand.Guest: Dr. Nathalie Vriend is an associate professor in mechanical engineering and leader of the Granular Flow Laboratory at the University of Colorado in Boulder.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 09/02
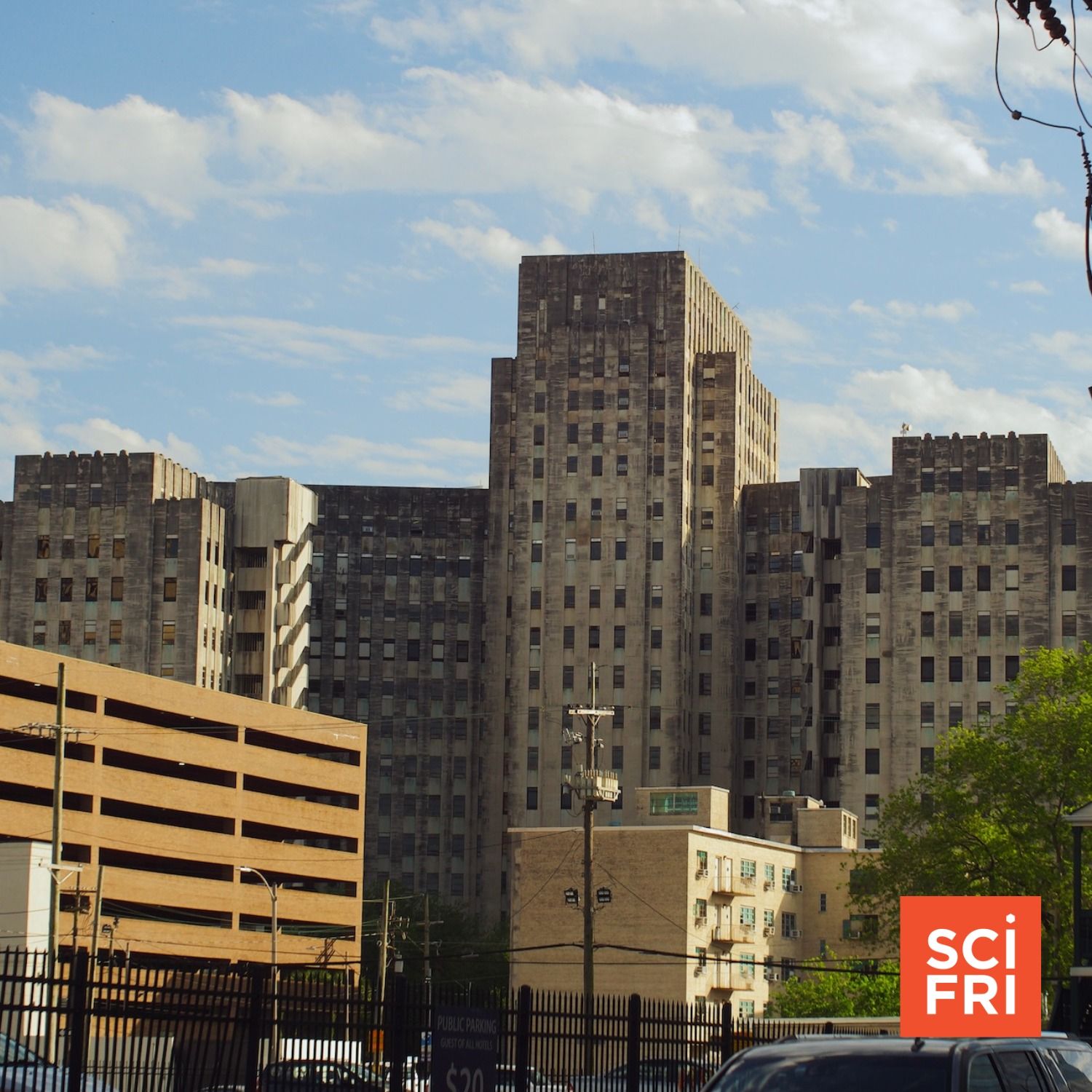 An ER Doctor Reflects On Hurricane Katrina, 20 Years Later
An ER Doctor Reflects On Hurricane Katrina, 20 Years LaterTwenty years ago, Hurricane Katrina made landfall in Louisiana, and the levees designed to protect New Orleans failed. Huge swaths of the city flooded, and 1,600 people were trapped inside Charity Hospital. Physician Erica Fisher was working in Charity’s emergency room at the time, and she and her colleagues fought for days to keep their patients alive.Host Flora Lichtman speaks with Dr. Fisher, now an emergency medicine physician at University Medical Center in New Orleans, about Hurricane Katrina and the vulnerability of our healthcare systems in the face of disasters.Plus, science writer Maggie Koerth joins Flora to share other science news the week, including the link between heat waves and aging, updated COVID vaccine guidelines, the ancient origins of human mucus, and the possibility that dwarf planet Ceres could once have sustained life.Guest: Dr. Erica Fisher is an emergency medicine physician at University Medical Center in New Orleans, Louisiana.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 08/29
 An Archaeologist And A Tattoo Artist Decipher Ancient Ink
An Archaeologist And A Tattoo Artist Decipher Ancient InkResearchers recently used near-infrared photography to get a detailed look at ancient artwork showing scenes of wild animals tangled in a fight. But these weren’t paintings on a cave wall. They were tattoos on the arms of a Siberian woman who lived 2,300 years ago. What can ancient ink tell us about our ancestors? Sticking and poking their way into this with Host Flora Lichtman are archaeologist Aaron Deter-Wolf and his research collaborator, tattoo artist Danny Riday.Guests: Aaron Deter-Wolf is an archaeologist for the Tennessee Division of Archaeology in Nashville, Tennessee.Danny Riday is a tattoo artist and independent researcher based in Les Eyzies, France.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 08/28
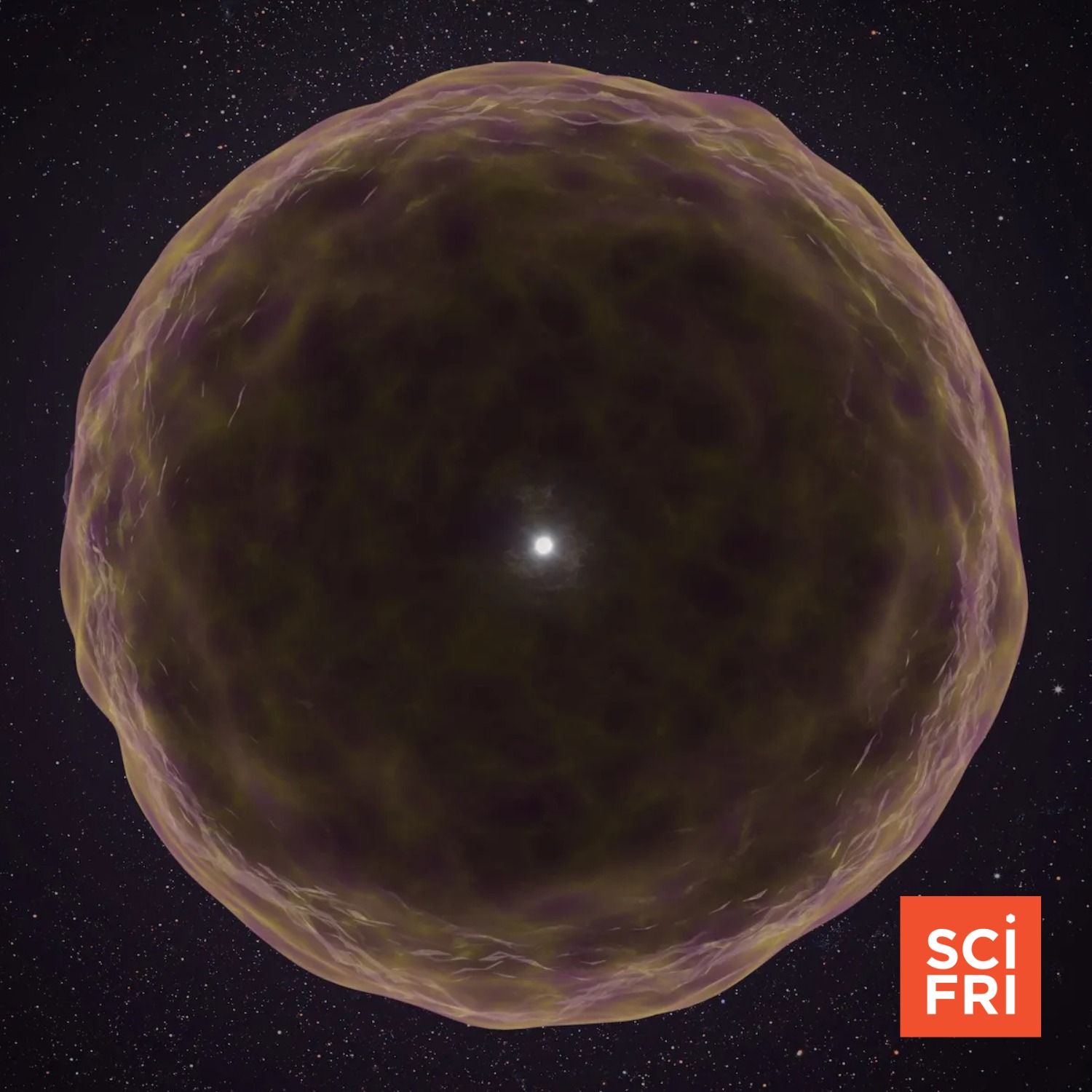 What Lies Beneath The Outer Layers Of A Star?
What Lies Beneath The Outer Layers Of A Star?You might think of a star as a mass of incandescent gas, a gigantic nuclear furnace where hydrogen is turned into helium at a temperature of millions of degrees. But researchers recently reported that they’d observed some of what lies beneath all that hydrogen and helium, at least inside one unusual supernova. The star, named supernova 2021yfj, had its outer layers stripped away, leaving behind a silicon- and sulfur-rich inner shell.Astrophysicist Steve Schulze joins Host Flora Lichtman to describe what the team spotted in the heart of a dying star.Guest: Dr. Steve Schulze is a research associate at Northwestern University’s Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics.Transcripts for each episode are available within 1-3 days at sciencefriday.com.
Subscribe to this podcast. Plus, to stay updated on all things science, sign up for Science Friday's newsletters.
Published 08/27